Understanding the design considerations for working platforms is crucial to ensuring heavy machinery operates safely and efficiently. This involves careful planning around stability, load capacity, and adaptability to different site conditions.
Here are some of the key design considerations for working platforms.
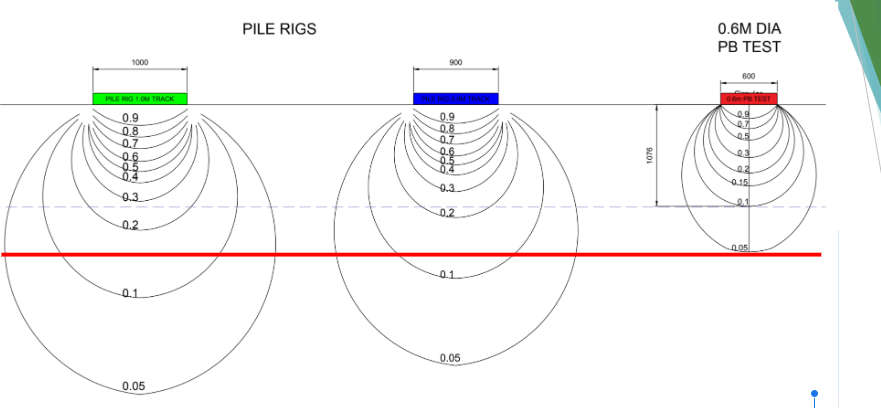
Stability for Machinery: Platforms must offer a stable and level base for machinery such as piling rigs and cranes when operating/tracking.
Deformation: Working platforms should be designed so that they do not deform excessively under heavy loads.
Durability: Due to environmental conditions, platforms need to be robust, using materials and construction methodologies that can sustain prolonged use.
Operational Compatibility: The design must accommodate the operational needs of the project, including the ability for machinery to perform specific movements without damaging the platform (i.e tracked plant to sprag)
Other design considerations may need to be incorporated depending on the use case that may include:
Load Support: Beyond primary machinery, platforms may need to support additional loads from scaffold foundations or other construction elements.
Ground Conditions Adaptation: An understanding of site-specific ground conditions is crucial, to ensure working platforms have a solid foundation and can handle the intended loads. Ground water can have a large impact on design solutions and its effect should not be underestimated.
Environmental Considerations: In environmentally sensitive or remediation sites, platforms might also need to prevent the spread of contamination, incorporating protective measures into the design.
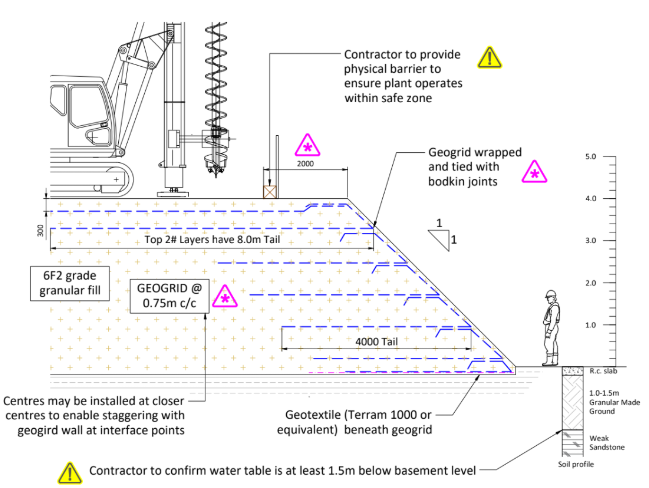
Sample drawing of a working platform design
Additional Resources
BRE 470 “Working Platforms for Tracked Plant”: Essential for understanding the design and construction of traditional working platforms, focusing on stability and safety.
Temporary Works Forum (TWf): Offers practical advice on temporary works, including platforms as part of their design guide on the subject.
CIRIA Publications: Including C765 and C718, provide detailed guidelines on ground support and investigation platforms, useful for platform design considerations.
Geosynthetics Institute (GSI): Useful for those using geosynthetics, offering research and case studies on effective material use.
Manufacturers’ Technical Support and Spec Sheets: For specific product insights and practical applications of materials like geogrids.